RFID Forklift

RFID on Forklifts
When equipping mobile forklifts with RFID systems, it is important to focus primarily on the main operating modes of the system:
- Coordinate grid
- Shadow control using barcodes
- Address-based cargo handling.
Integration purpose
- Automatically record the fact of pallet movement.
- Link RFID data to a specific order/location/storage area.
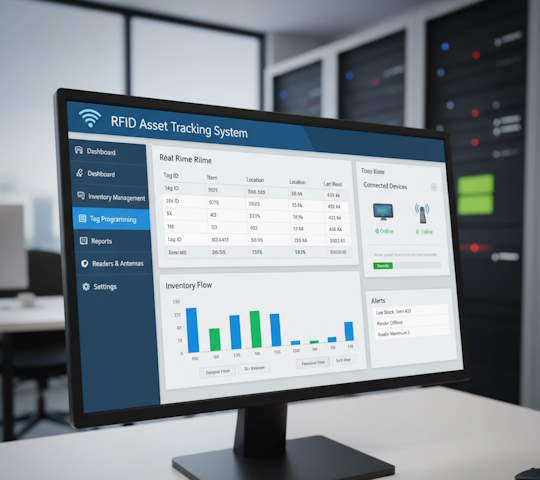
- Transmit real-time movement data of cargo and forklift to WMS or ERP.
What is needed for integration
- Forklift with power supply for additional equipment.
- UHF RFID reader (for example, Impinj Speedway R420)
- Antenna (usually 1–2 antennas are installed: on the carriage and under the forks)
- Software for RFID and WMS/ERP system integration
- Industrial tablet or mobile data terminal (MDT).
- Wi-Fi or 4G module — for connecting to the WMS/ERP server
Integration logic
- Storage locations and forklift movement coordinates are permanently marked with RFID tags (UHF).
- Containers (pallets, bins) are permanently marked with RFID tags (UHF).
- Pallets are marked with temporary-use RFID tags (UHF).
- The forklift lifts the pallet — the tag enters the antenna’s read zone.
- The reader scans the tag ID and sends it to the WMS or ERP software with display on the data terminal.
- The software on the tablet matches the read ID with the task from WMS/ERP/SAP.
- Action data (lifting, movement, location) is sent:
- To WMS (1C:WMS, SAP EWM, Manhattan, Oracle) via REST API or web service.
- To ERP — usually via HTTP service or published web service.
How it works in BAS or SAP
The configuration includes a “Tags” directory — each RFID tag is linked to a specific item/pallet. The service receives a POST request with the tag ID and current coordinates/location. A trigger records the event: “Moved to Location №”. In BAS, the movement history is visible in real time. In SAP EWM: RFID is read through middleware (for example, SAP Auto-ID Infrastructure — AII). Data is transferred to EWM via RFC or PI/PO. Processing rules (Warehouse Monitor) automatically create a Task (WT) for recording.
Depending on the operating mode, reader and antenna placement points are selected, as well as the RFID system and WMS operating algorithms. When purchasing forklifts, choose models:
- With CAN-bus or telematics support.
- With the ability to install RFID readers (fixed or mobile).
- With software integration capability (API, SDK).
Mobile forklifts most commonly chosen for warehouses with RFID/WMS integration.
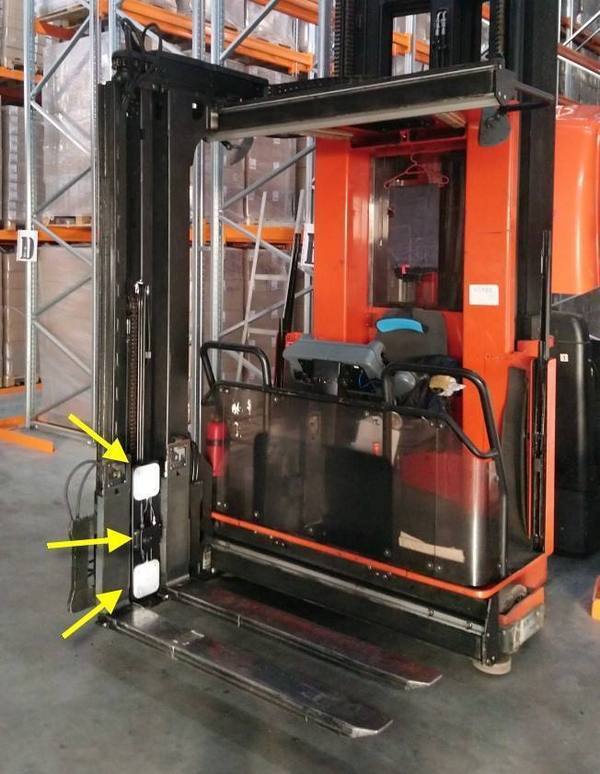

Electric Forklifts (Counterbalance Forklift). The most popular type for warehouses with RFID. Well suited for indoor areas. Electronics are easily integrated with RFID readers, antennas, and WMS. They often have a telematics module installed by default. Examples of popular series:
- Toyota Traigo (8FBE, 8FBMT) Load capacity: 1.0–3.5 t. Low noise level, CAN-bus, ready for sensor installation.
- Linde E20–E35 (series 386/387). High ergonomics. Option to install cameras, RFID, scanners.
- Jungheinrich EFG series 3/4. Integration with Jungheinrich Fleet Management. Ready for IoT and WMS.
- Crown SC 6000. Modular system. InfoLink telematics — can connect RFID.
Reach Trucks. Reach trucks are often used for medium and high racking. RFID readers are installed on the carriage for precise positioning. Operate in narrow aisles. Popular series:
- Jungheinrich ETV series 2/3
- Linde R14–R20
- Crown ESR series
- Toyota BT Reflex
Stackers and Order Pickers. Used for picking and labeling goods. RFID readers are most often mounted on the forks or on the operator’s tablet. Examples:
- Crown WAV 60 (Wave Work Assist Vehicle). Popular for e-commerce.
- Linde V Modular. High-level order picker.
- Jungheinrich EKS series.
Diesel and Gas Forklifts. Less common indoors but relevant for outdoor docks. Can also be retrofitted with RFID. Examples:
- Toyota Tonero (IC Engine)
- Hyster H2.0–3.5FT
- Doosan G20/25
Key points for RFID integration
- Wide roof and cabin: space for installing an antenna or reader.
- CAN-bus or optional port: simplifies connection of external modules.
- 12/24V sockets or built-in UPS: power supply for RFID equipment.
- Software gateway: telematics or API for transferring data to WMS or ERP.
Practical application
In practice, forklifts are most often equipped with:
- Fixed RFID reader with an Impinj Speedway antenna. Mounted on the mast or carriage.
- Mobile data collection terminal with RFID — operator scans tags manually.
There is no universal or standard solution for equipping a forklift with an RFID system and integrating it with a warehouse accounting and management system. Each project and request requires an individual approach: it is necessary to carefully select locations for installing readers, determine the types and locations of RFID tags for marking storage locations (RFID coordinates), containers and cargo. After selecting the equipment and marking, pilot tests are carried out under real operating conditions. Based on the testing results, the necessary adjustments are made, and a decision is made to scale the solution to the entire fleet of forklifts and fully equip racks and containers with RFID tags.
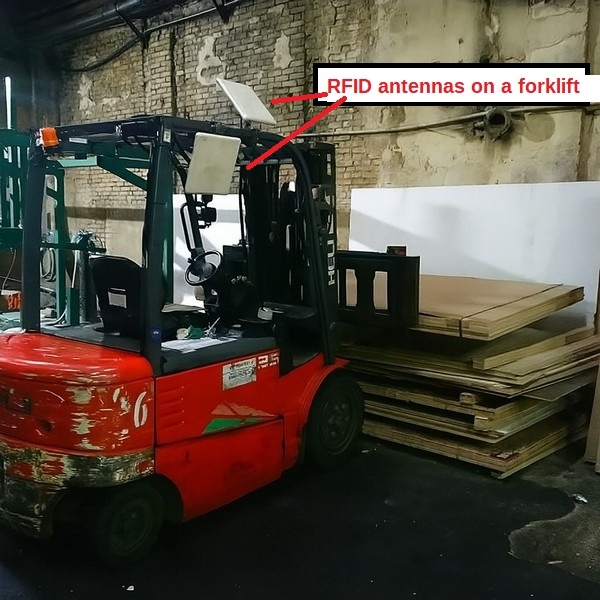

Successful integration examples
Jungheinrich EFG + Impinj Speedway R420 — a classic for pallet warehouses.