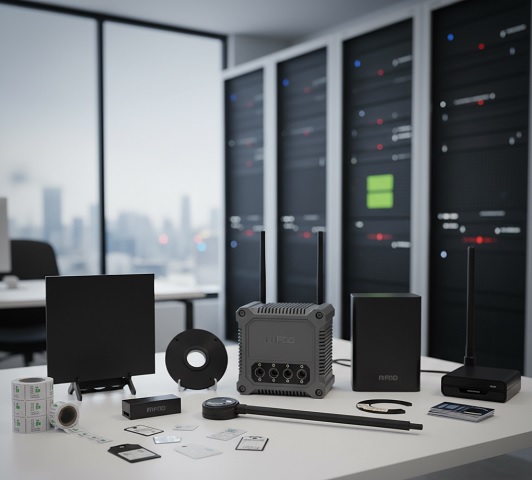
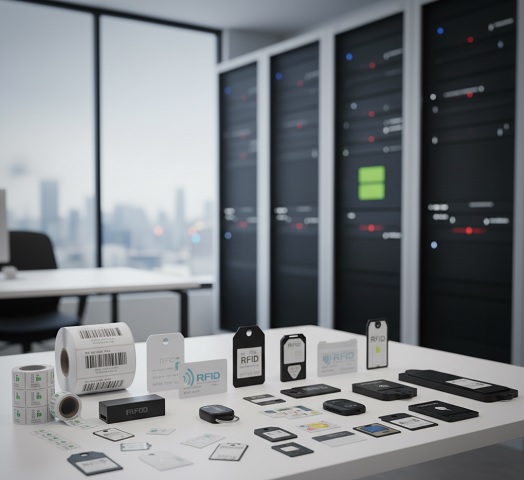
RFID Tag Mounting Methods
RFID Tag Mounting Methods
Summary of English-language best practices: choose the tag for the surface, mount for the environment, and always test after installation.
| Mounting Method | Advantages | Limitations | Typical Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adhesive backing (3M tapes, stickers) | Quick install, low cost, no tools required. | Limited durability in heat/moisture/chemicals; requires clean, flat surfaces. | RetailLogisticsPackagingWarehousing |
| Mechanical fasteners (screws, rivets, bolts, cable ties) | High strength and reliability for outdoor/industrial use. | Needs drilling/mounting holes; not for delicate assets. | AutomotiveRailConstructionHeavy Equipment |
| Embedding / inlay (into plastic, rubber, part body) | Permanent, protected, tamper-resistant. | Usually only at manufacturing stage; not serviceable. | TiresRTI/ContainersToolsIndustrial parts |
| Encapsulation with epoxy / resin / potting | Resists vibration, impact, moisture, and chemicals. | Non-removable; adds cost and weight. | Oil & GasMiningChemicalEnergy |
| Welding / heat staking | Extremely durable; integrated with metal/plastic body; tamper-proof. | Requires specialized tools/process; irreversible. | Automotive componentsMachineryDefense |
| Sewn-in / woven (textiles and apparel) | Invisible and integrated; washable cycles supported (with proper tags). | For fabrics only; read range may reduce if deeply hidden. | ApparelUniformsLaundries |
| Magnetic mounting (reusable holders) | Tool-less, removable/reusable; no surface damage. | Only for ferromagnetic surfaces; can shift with vibration. | Temporary taggingMetal shelvingWarehouse assets |
| Clamps / brackets / protective holders | Adjustable, reusable; adds protection from impact. | Extra hardware; increases size/weight. | PalletsRacksLogistics containers |
Notes: Select on-metal tags for conductive surfaces; align tag orientation to reader antenna; avoid RF shadowing; consider high-temp/UV/chemical resistance as needed; test performance after installation.